Applications
Life changing applications
Bioprinting organs, coating medical implants, and enabling animal-free drug screening—Black Drop powers the future of biomedical innovation.
Regenerative Medicine
Our bioprinting solutions support regenerative medicine by enabling the creation of patient-specific tissues and organs, aiming to reduce reliance on donor transplants and improve healing outcomes.
In Blind Zero Project University of Heidelberg uses Black Drop printer to print human cornea transplants.
Featured Black Drop Products
DoD-printing of 3% Blue Drop Agarose (35 °C) onto cooled platform using the Black Drop Regenate.
Drug discovery
We provide advanced bioprinting tools like bioprinting-specific Organ-Chips that facilitate the development of more accurate and efficient drug testing models, accelerating the discovery of new therapeutics.
Featured Black Drop Products
DoD-printing of 7 drops of X% Blue Drop Alginate (37 °C) into BioVOC organ chip using the Black Drop Regenate.
Related Publication:
Perfusable Tissue Models
Perfusable Tissue Models unlock new possibilities in medical research by providing lifelike, vascularized tissues that can be perfused at physiological conditions. Using the Regenate bioprinting system, the production of your perfusable tissue models can be automated at a high accuracy. Our STL-based slicing algorithms give you the freedom to produce a wide variety of custom-designed channel geometries.
Featured Black Drop Products
Multi-head pneumatic extrusion of 5% Red Drop Gelatine and 30% Pluronic F127 (colored with fluorescent dye) using the Black Drop Regenate.
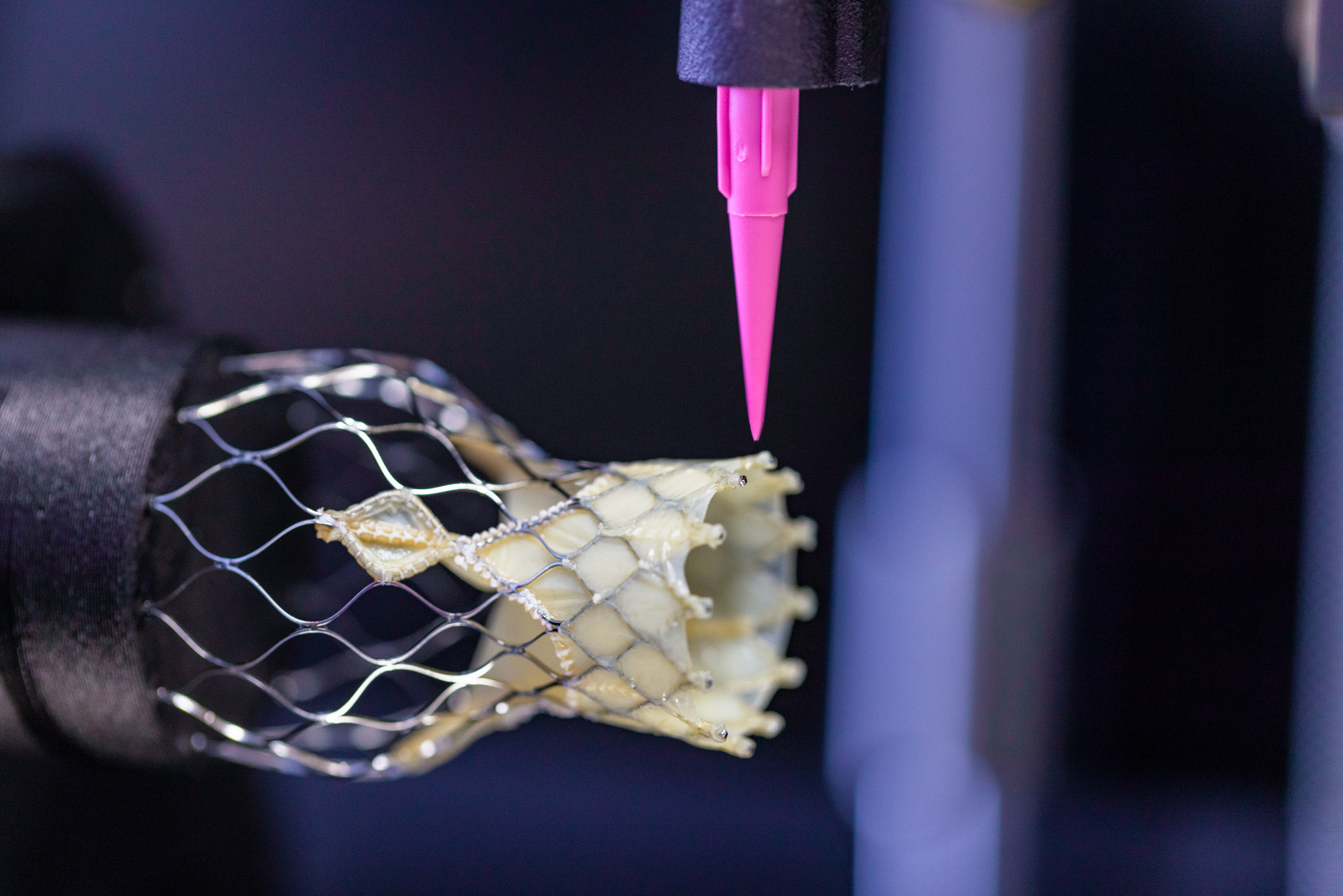
Biologization of medical Implants
Our technologies enable the engineering of complex biological structures on top of existing medical implants, contributing to faster integration with less rejection reactions improving patient care.
Cell Spheroids and Hydrogel Beads
Cell spheroids replicate the 3D structure and microenvironment of living tissues more accurately than 2D cell cultures. Relying on cellular self-assembly, they provide more realistic models to study cell growth, differentiation, and interactions under standardized conditions. This makes them especially valuable for cancer research, drug development, and regenerative medicine.
Hydrogel beads provide a biocompatible and tunable 3D environment for encapsulating cell specific nutrients or drugs to manipulate cell behavior. They allow precise control over nutrient and drug diffusion, making them ideal for studying indirect cell interaction and therapeutic delivery. Their versatility makes them useful in tissue engineering, drug screening, and regenerative medicine.
Featured Black Drop Products
DoD-printing of 2% Blue Drop Alginate (37°C) into 10% AlgiX crosslinking bath using the Black Drop Handheld Bioprinting Station.
Handheld Bioprinting
Bioprinting with the Black Drop handheld station allows you to precisely deposition cells and biomaterials right where you want them to be. Contactless handheld printing reduces damage and contamination risk, while extrusion handheld printing lets you produce tissue models just like using a pen.
For labs accustomed to 2D cell culture, it simplifies the transition to 3D models by providing an intuitive, flexible way to build simple structured tissues without complex machinery or protocols.
It also accelerates hydrogel matrix development and testing by enabling rapid, small-scale prototyping of different formulations directly in the culture environment, allowing researchers to quickly evaluate cell viability, distribution, and matrix performance.
Featured Black Drop Products
DoD-printing of a vascular branch using 2% Blue Drop Alginate (37°C) with the Black Drop Handheld Bioprinting Station.
Research
Science Proofed
From engineered living materials to next-generation biofabrication tools — discover the groundbreaking publications shaping Black Drop’s contribution to science and innovation.

Publications
Selected Publications demonstrating Black Drop Technology


Modified Bioink Platform for 3D Bioprinting
In Fiber4Ink we explore a novel, modular bioink platform that combines protein-based hydrogels, such as collagen, with polymeric microfibers. This design enhances the mechanical and rheological properties of the bioink while enabling precise control of cell behavior on topographical, molecular, and electro-mechanical levels.
The bioink platform is tested with various cross-linking mechanisms (physical, thermal, light-based) and 3D bioprinting techniques (direct bioprinting, stereolithography, microfluidic printing). Novel hard- and software solutions like 2-component mixing are explored to manipulate the embedded fibers while printing. This allows to control spatial cell alignment (creation of anisotropic tissues), cell type-specific drug delivery, electrical signal transmission while providing improved nutrient supply.
A key objective is the creation of a functional neural cell model, paving the way for innovations in regenerative medicine, tissue models for the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, and cell-based food production.
Partners
Funded by:
Project Management:
Duration:


Wireless 3D-Bioprinted Mesh for Targeted Neural Regeneration
Piezo4Spine is an EU-funded Horizon Europe Pathfinder project aiming to transform treatment options for spinal cord injury (SCI), a condition that often results in paralysis and has no current cure. The project develops a novel 3D bioprinted mesh embedded with bioactive nanocarriers, enabling controlled, wireless release of therapeutic agents directly at the injury site.
By combining mechanotransduction-based stimulation, gene therapy, and advanced biomaterials, Piezo4Spine targets multiple cell types within the spinal cord to overcome barriers such as inhibitory scarring and limited axon regeneration. This multidisciplinary approach aspires not only to enable functional recovery after SCI but also to open new therapeutic pathways for a broad range of neural and non-neural disorders.
Partners
Funded by:


RUBIN-reACT
reACT (Resorbable Medical Solutions from the Aachen Technology Region) is an ambitious collaborative project under the RUBIN funding program, initiated by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF). The program aims to enhance strategic cooperation between companies, universities, and research institutions, fostering regional innovation, value chain development, and the creation of groundbreaking products and services.
Project Focus:
The primary goal of the reACT project is to address the critical clinical need for temporally adaptive, partially resorbable endoluminal support structures, specifically stents, for cardiovascular care. In Germany alone, approximately 300,000 patients live with congenital heart disease, with at least 20% requiring heart valve replacement during their lifetime. Current bioprostheses, such as homografts and xenografts, often suffer from reduced durability due to early calcification, leading to multiple repeat surgeries. This issue is particularly significant for children, whose heart valves must adapt to growth and increasing hemodynamic demands.
Innovative Approach:
The reACT project leverages the innovation potential of new resorbable materials, such as resorbable metals combined with non-resorbable materials and adaptive hydrogels. These materials are integrated using advanced manufacturing processes, including 3D printing and textile technology. The project also benefits from the specialized application knowledge of clinical partners to develop partially resorbable vascular implants that can adapt over time.
Partners
Funded by:
Project Management:
Find yourself in a use case?
Let’s talk about opportunities.